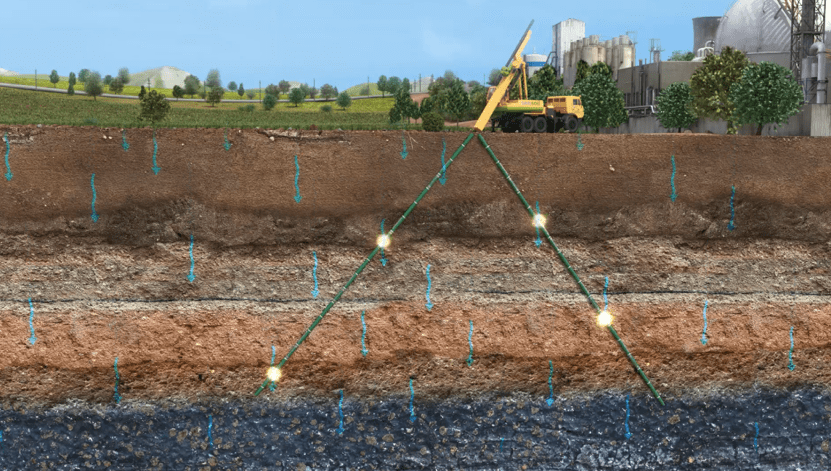
Groundwater Recharge
Groundwater recharge (GR) refers to the process by which water infiltrates down from the land surface through the unsaturated zone to the aquifer below.
Assessment of the quality and quantity of groundwater recharge is essential for water resources management. This is true especially today due to climate change’s impact on global warming and reduction in precipitation.
Groundwater Recharge Sources, Rate and Quality
The primary source of recharge is attributed to precipitation and deep-water percolation through the soil and deep unsaturated zone to the underlying aquifer. Yet, other sources of recharge include infiltration of surface water runoff, irrigation water, and infiltration of treated wastewater through infiltration basins.
The rate and quality of groundwater recharge depend on various factors, such as land use, soil type, vegetation cover, and climate conditions. Human activities, such as agriculture, industry and urbanization also have significant impact on the quality and rate of groundwater recharge.
Real time Measurement of the Recharge Process
Sensoil’s Vadose zone Monitoring System (VMS) provides continuous real-time data on quality and quantity of water percolation across the unsaturated zone. It is based on continuous measurement of variations in sediment moisture and chemical composition from land surface to the water table. Thus, VMS provides a very powerful tool for real time measurement of the recharge process.
Sensoil's Vadose Zone Monitoring System: Well Established Technology
Sensoil’s VMS is well established monitoring technology, with over 150 worldwide installations on five continents. VMS is used for a variety of applications in a wide range of hydrological and geological setups. Installation setups include measurements of groundwater recharge under different land uses, as well as impact of agriculture on groundwater quality, remediation of contaminated sites and monitoring earthen dam (levee) stability.